Case Study: DWaste Edge AI for Recycling at UMD
The DWaste edge device is a compact AI system designed to monitor waste disposal in real time. It uses computer vision to identify and quantify different types of waste, helping institutions understand disposal patterns, reduce contamination in recycling streams, and improve sustainability practices. The device was developed to make waste auditing faster, more accurate, and scalable without manual inspection.
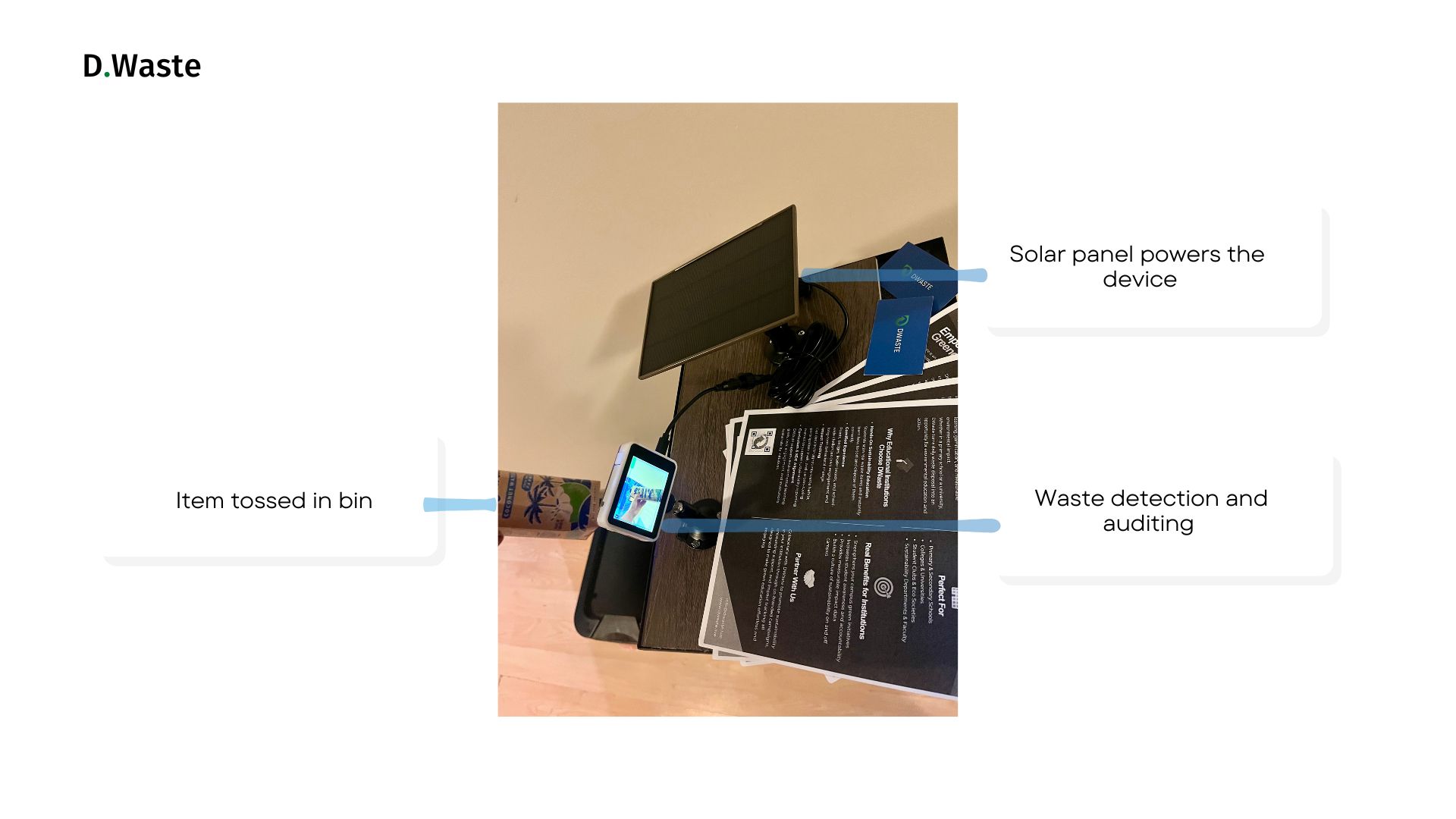 DWaste edge device capturing a waste item in real time
DWaste edge device capturing a waste item in real time
Case Study Context: Mixed Recycling at UMD
At the University of Maryland (UMD), recycling is implemented through a mixed recycling system, where materials such as metal, plastic, paper, and cardboard are collected together in a single blue bin. This system simplifies disposal for users and encourages participation, but it limits visibility into what is actually being recycled at the item level.
 Signage showing items accepted in the blue recycling bin
Signage showing items accepted in the blue recycling bin
Because recyclable materials are mixed at the point of disposal, institutions typically rely on downstream audits, estimates, or occasional manual sorting to understand recycling composition. These methods are not designed to provide continuous or location-specific insight, making it difficult to quantify disposal patterns or identify which materials dominate the recycling stream.
This case study examines how deploying the DWaste edge device directly at the bin level can introduce item-level visibility into an existing mixed recycling system without changing infrastructure or user behavior. By capturing each disposal event in real time, the deployment enables measurable, data-driven insights into recycling behavior in a live campus environment.
We conducted this experiment to evaluate the device’s performance in a real-world setting and to understand which recyclable materials are most commonly disposed of. The goal was to assess how edge AI can support institutions in optimizing waste reduction initiatives and improving recycling outcomes.
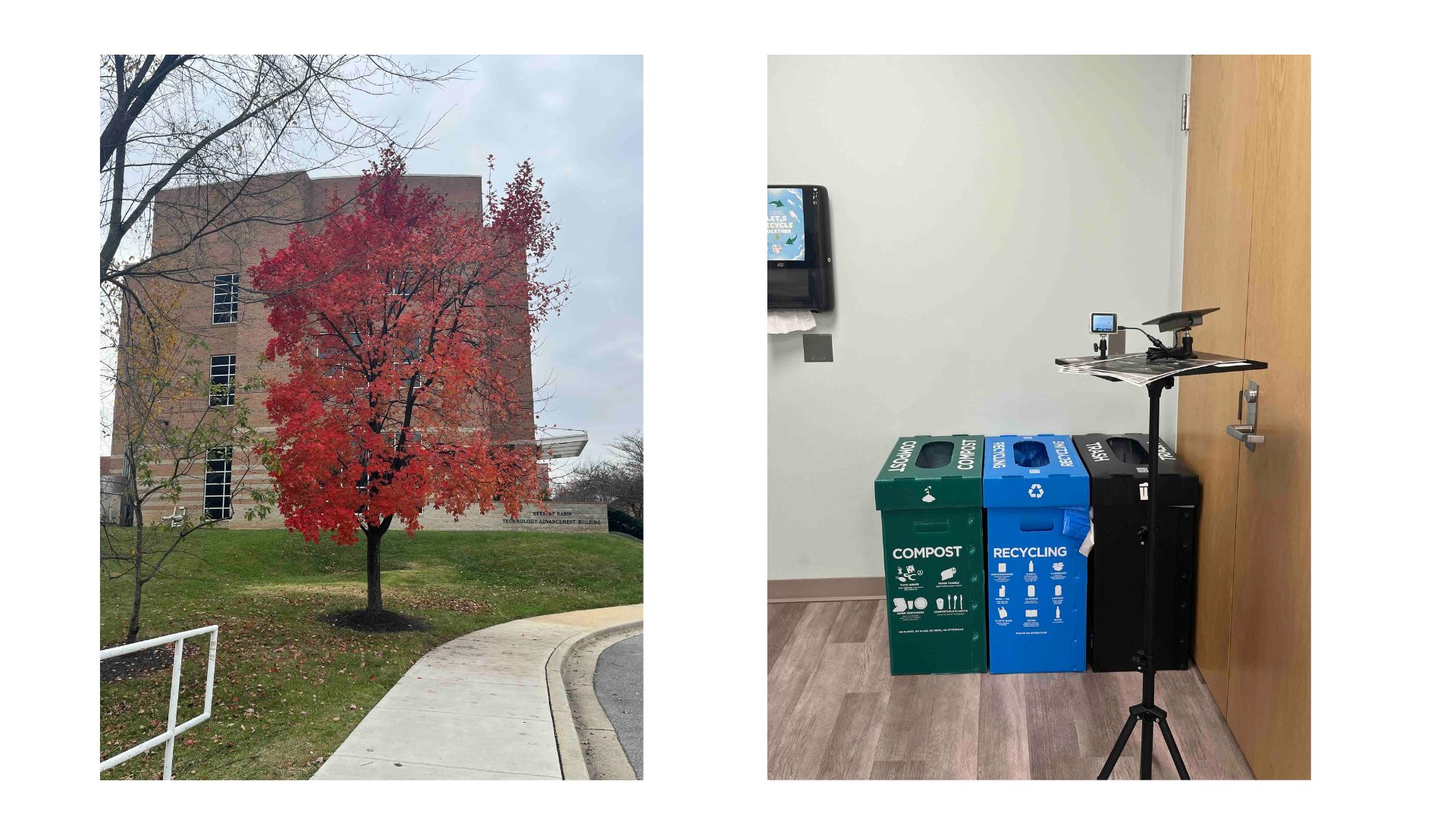 DWaste edge device deployed near recycling bins at Herbert Rabin Technology Advancement Building
DWaste edge device deployed near recycling bins at Herbert Rabin Technology Advancement Building
The deployment took place in a co-working space at the Herbert Rabin Technology Advancement Building, University of Maryland (UMD). MTech Ventures supported this initiative by assisting with device placement. The device operated for one month, from November 19 to December 19, 2025, recording all items disposed of in the bins.
The space contained three hallway bins: compost, recycling, and trash. Each bin had clear signage and measured 32 gallons (14 inches deep, 22 inches wide, 29 inches tall). For this deployment, the DWaste edge device was powered by a solar panel and mounted on an adjustable tripod stand, allowing flexible positioning. The camera was focused specifically on the bins and the act of waste disposal.
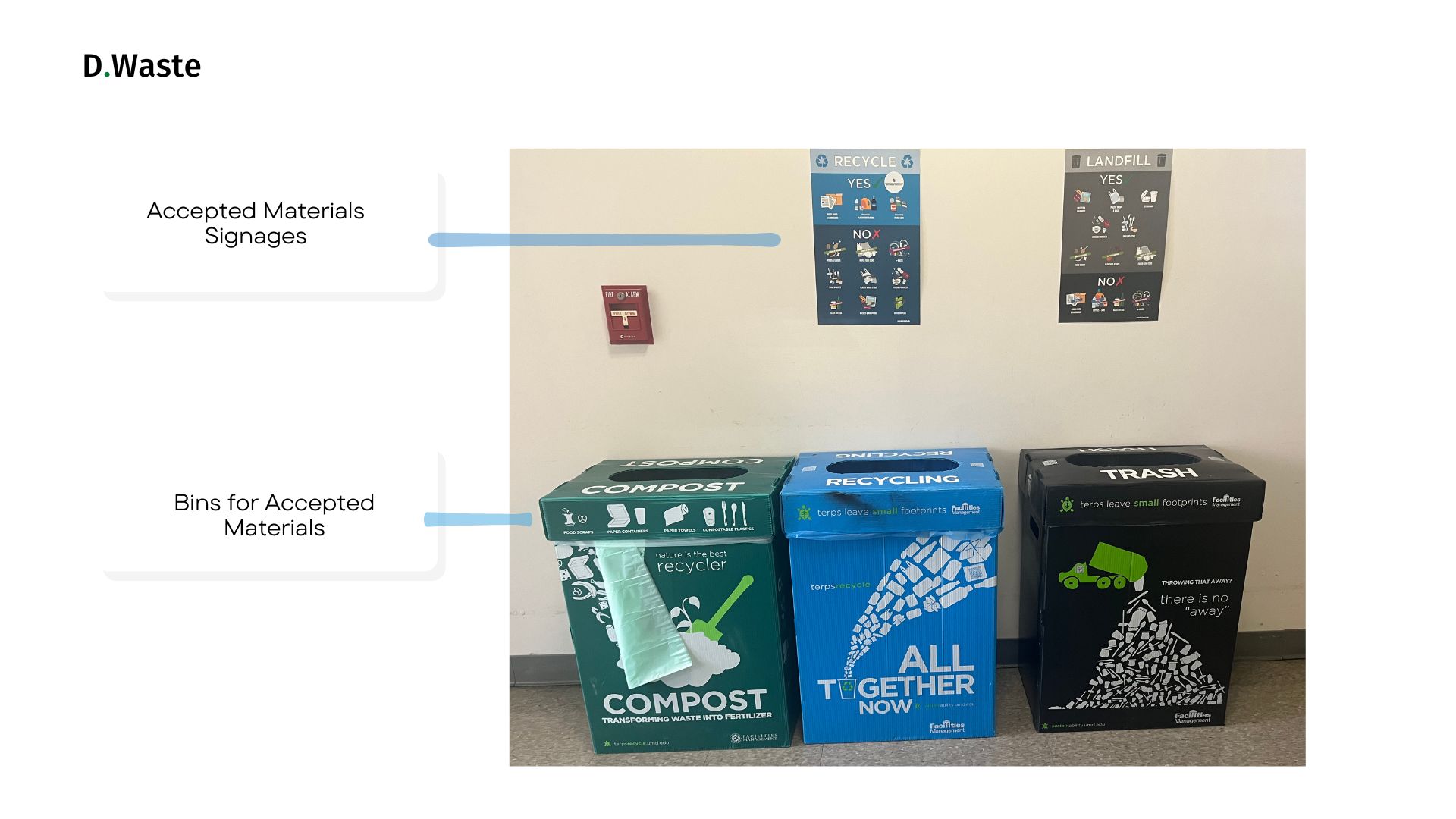 Compost, recycling, and trash bins in the hallways
Compost, recycling, and trash bins in the hallways
The experiment focused on recyclable items in the blue bins: metal, cardboard, plastic, and paper, which are accepted for mixed recycling at UMD. Each disposal event was recorded by the DWaste device, creating a detailed and continuous view of recycling behavior.
 DWaste edge device capturing each disposal for data analysis
DWaste edge device capturing each disposal for data analysis
Over the month-long deployment, the device recorded the following recyclable items:
Metal
14
Plastic
21
Paper
18
Cardboard
23
Cardboard emerged as the most commonly disposed recyclable material, followed by plastic. These results provide a holistic view of recycling behavior within a mixed recycling system and highlight opportunities for targeted education and waste reduction efforts.
This case study represents a snapshot of recycling behavior at a single location over a limited period. While results may vary across sites and some items may not have been detected, the deployment demonstrates that the DWaste edge device can deliver real-time, item-level insights from mixed recycling streams. These insights can support institutions in designing more effective sustainability initiatives, improving recycling campaigns, and reducing contamination across waste systems.
Published : Dec 24, 2025
Waste Management
Edge AI
Sustainability
Recycling