Manage Household Waste using Open Source Data
Waste management is a major issue in our modern society. The increasing population and consumption lead to more waste being generated. The traditional method of disposing of household waste through landfilling or incineration is not sustainable in the long term. Using open-source data and a deep learning approach, a mobile app can manage household waste in an innovative way.
The global average of municipal solid waste generated per capita is 0.74kg per day, but in high-income countries like the United States, it can be as high as 2.1kg per day. Proper waste management is essential to reduce the negative impact of household waste on the environment and human health, given the significant amount of waste generated every day.
Mobile Apps and Open Source Data
Accessibility, collaboration, transparency, flexibility, security, and innovation are essential factors for creating successful and effective mobile apps that can be provided by using open source. OpenLitterMap and TrashOut apps are utilized for waste management and have made their source code accessible to the public.
DWaste is an open source mobile application that uses deep learning algorithms to classify and sort household waste. The app’s primary function is to enable users to take a photo of their waste and provide them with information on how to dispose of it properly. Various publicly available data sets such as TrashNet, Garbage Classification Data, and Garbage Classification V2 can be used in waste classification.
Inner Mechanics of DWaste
In DWaste, they use the TrashNet dataset and measure its performance with various state-of-the-art machine learning models: InceptionV3, MobileNetV2, InceptionResnet V2, ResNet, MobileNet, and Xception to learn and predict the type of waste.
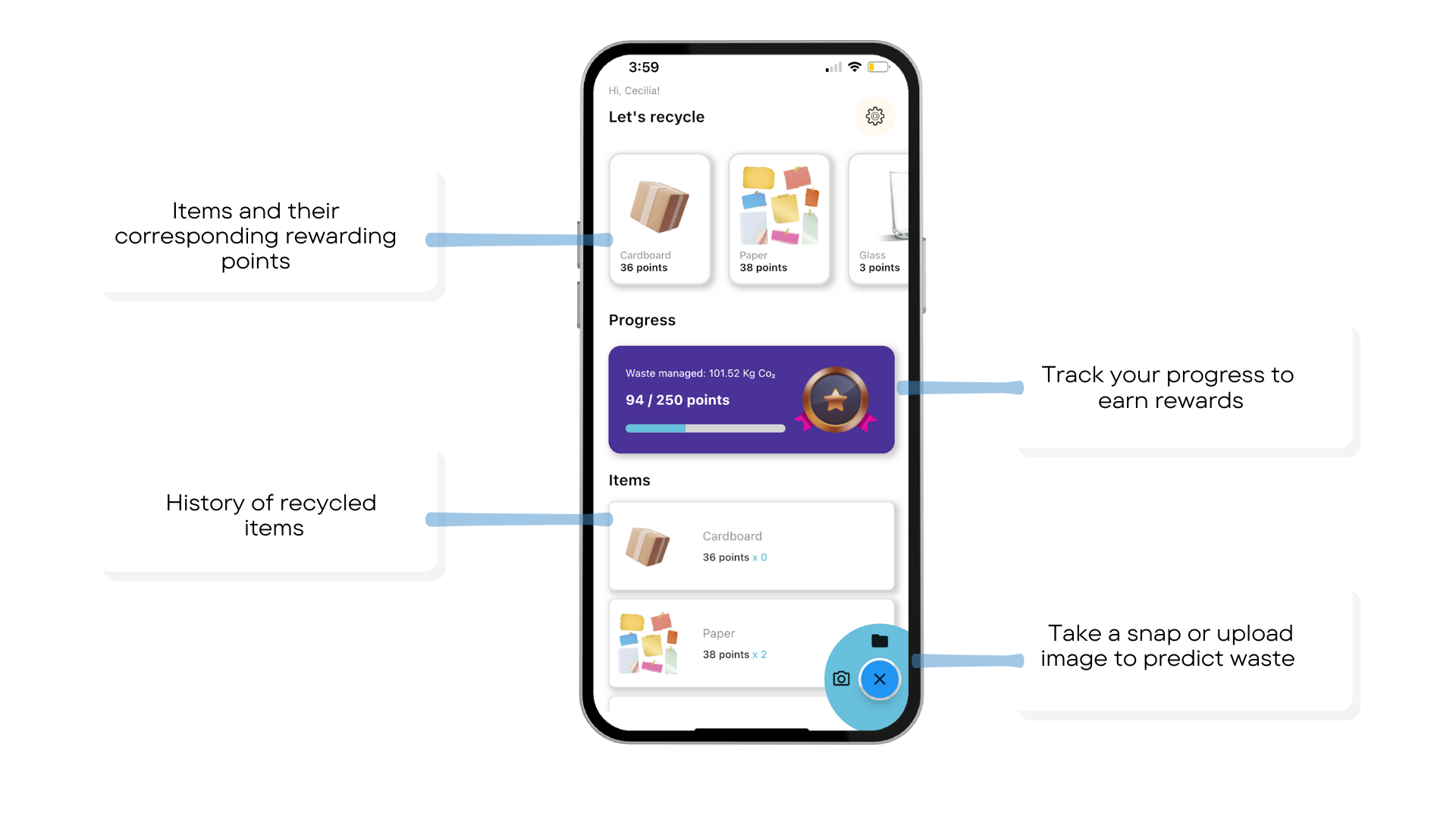 DWaste App, Suman Kunwar, CC BY-SA 4.0
DWaste App, Suman Kunwar, CC BY-SA 4.0
The app utilizes deep learning algorithms to recognize various types of waste, including plastics, glass, paper, and organic waste, based on the provided training data. Additionally, it can provide information on where to dispose of the waste and what recycling options are available. This approach can be customized to the user’s specific needs, including local waste management regulations and individual household waste disposal habits and preferences.
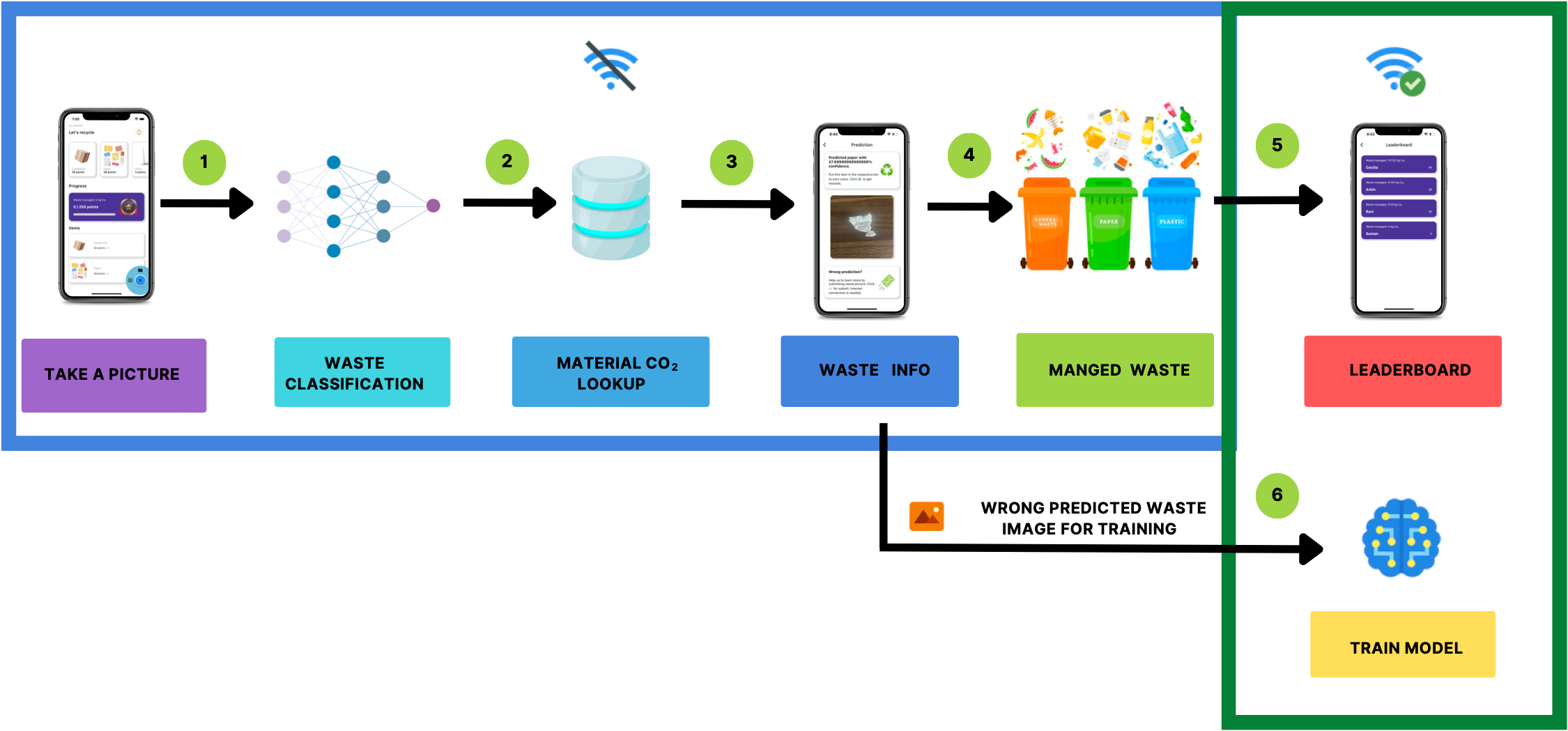 DWaste App Workflow, Suman Kunwar, CC BY-SA 4.0
DWaste App Workflow, Suman Kunwar, CC BY-SA 4.0
The classification models are then converted into a lite format, such as TFLite, which allows them to be used on mobile devices with limited resources. The lite format enables fast loading times, smaller size, and compatibility with various programming languages and platforms.
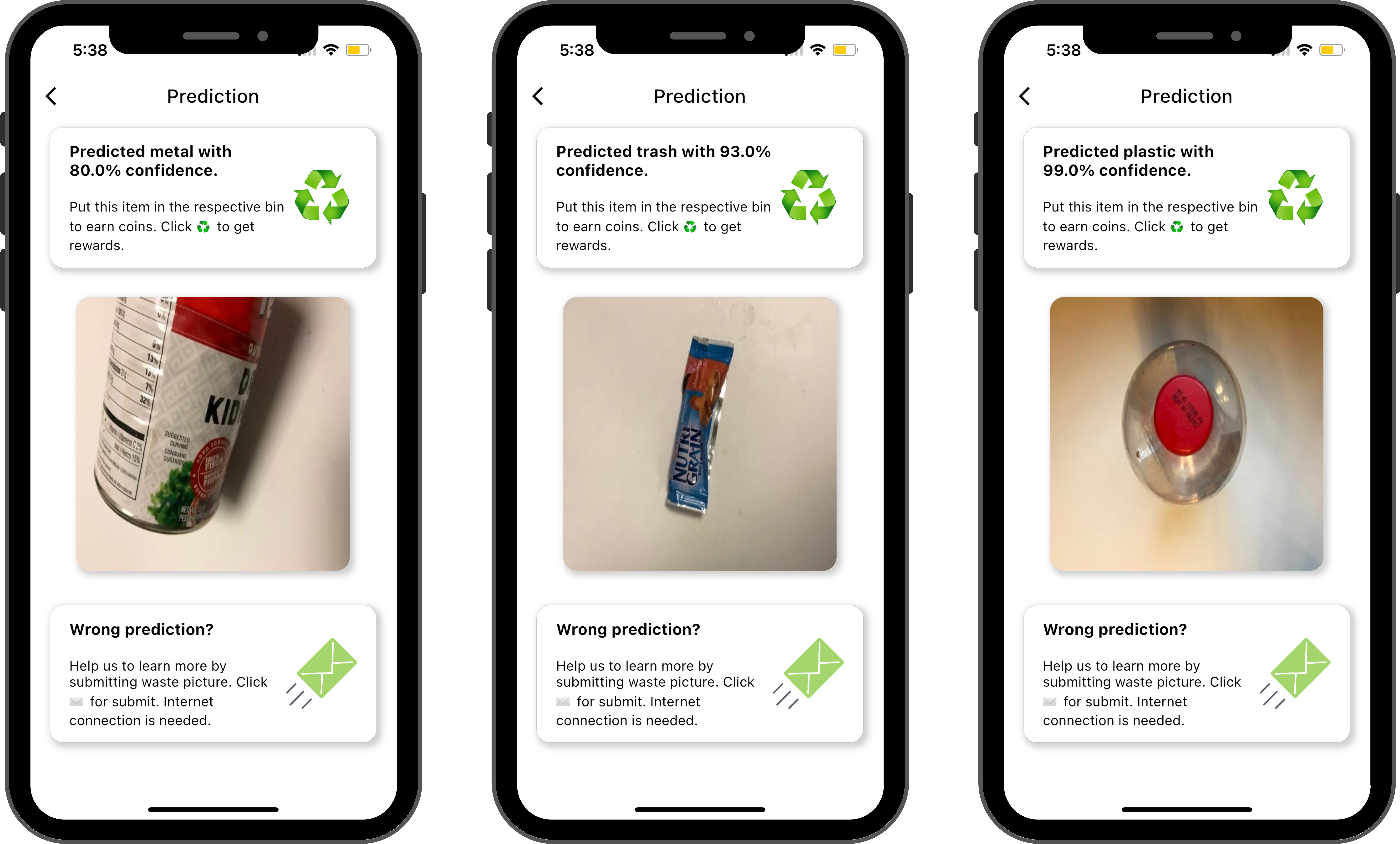 Waste Classification Results, Suman Kunwar, CC BY-SA 4.0
Waste Classification Results, Suman Kunwar, CC BY-SA 4.0
The app’s user interface is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, making it easy for anyone to use, and can also be used in conjunction with other waste management services, such as waste collection and recycling services. Leaderboard is also generated based on the CO2 preserved by recycling/composting. The app can help households reduce the amount of waste they generate, increase their recycling rate, and reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
Problems in waste classification via image
Classifying waste based on its image is challenging due to the varying composition of materials that can impact its recyclability or compostability, as well as the shapes and sizes of waste and the capabilities of local recycling centers. To ensure effective classification, it is necessary to establish a monitoring and improvement mechanism, such as feedback collection, additional data training, and leveraging advanced tools and technologies. So, continuous learning from new data and use of the state of art tools and technology makes the app more accurate and efficient over time. This ensures that the app can adapt to changes in waste management regulations and changes in household waste composition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the deep learning approach using open-source data to manage household waste through a mobile app is a promising solution to the growing waste management problem. It can help households reduce their waste generation, increase their recycling rate, and ultimately reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. The app’s user-friendly interface and ability to adapt to changes make it a powerful tool in the fight against waste.
Resources:
-
iOS: https://apps.apple.com/app/deep-waste-ai/id6445863514?platform=iphone
-
Android: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.hai.deep_waste
-
Source code: https://github.com/sumn2u/deep-waste-app
-
Paper Link: https://www.aimspress.com/article/doi/10.3934/ctr.2023008
Published : May 27, 2023
Household Waste
Open Source data
Sustainability
Deep Learning